India’s missile capabilities represent a crucial aspect of its national defence strategy, showcasing the nation’s technological advancements and strategic foresight. With a diverse range of missile systems developed over decades, India aims to enhance its military readiness and maintain a balance of power in the region. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the various types of missiles in India, their features, significance, and the broader context of their development.
Understanding Missile Systems
Missiles, often referred to as guided missiles, are self-propelled weapons designed for precision targeting. They typically consist of five main components: the guidance system, targeting system, flight system, engine, and warhead. The integration of these components determines the missile’s effectiveness in delivering payloads to designated targets.
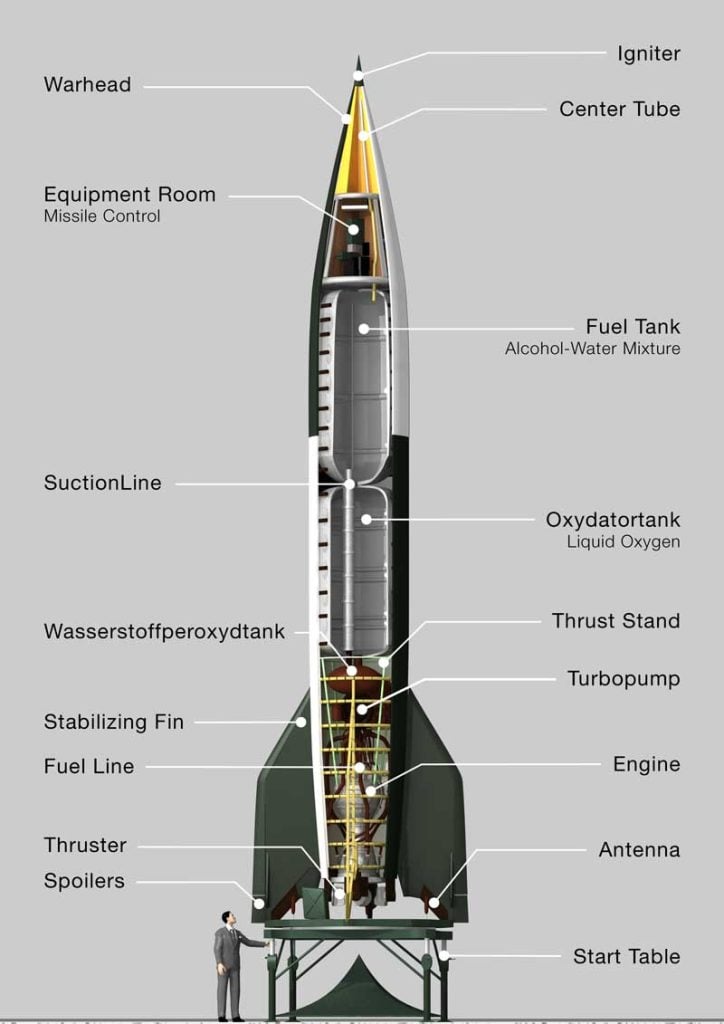
Key Components of Missiles
- Guidance System: This element ensures the missile follows a calculated trajectory towards its target, utilizing technologies such as GPS, inertial navigation, or radar.
- Targeting System: It identifies and locks onto the target, allowing for precise engagement. This can include laser guidance or image recognition systems.
- Flight System: The mechanism that propels the missile, which can be powered by solid or liquid fuels, significantly influences its range and speed.
- Engine: The propulsion system, whether a rocket motor or jet engine, determines how quickly and efficiently the missile can travel.
- Warhead: The payload carried by the missile, which can vary from conventional explosives to nuclear warheads, depending on the missile’s purpose.
Understanding these components is essential for grasping the capabilities and strategic importance of India’s missile arsenal.
Hallmarks of India’s Missile Development
India’s missile systems are characterized by several notable features that enhance their operational effectiveness:
High Accuracy
India’s missile technology incorporates sophisticated guidance systems that enable high precision in targeting. Advanced navigation technologies like inertial navigation and satellite guidance ensure that missiles can strike with minimal collateral damage.
Quick Reaction Capabilities
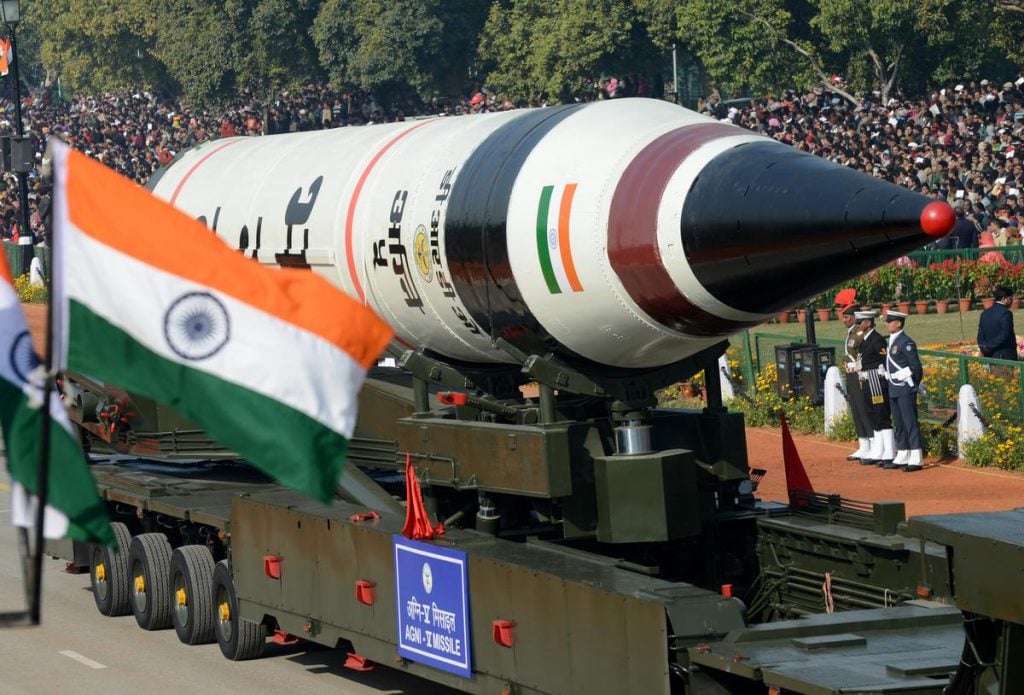
Many of India’s missiles are designed for rapid deployment. Utilizing solid propellants allows for shorter preparation times, enabling the armed forces to respond swiftly to emerging threats. For instance, the Agni series can be launched within minutes from mobile platforms.
Lethality and Range
The lethality of Indian missiles is augmented by powerful propulsion systems that extend their range and increase the payload capacity. Missiles like BrahMos, renowned for their supersonic speeds, exemplify this capability, making them formidable options for both offensive and defensive operations.
Overview of India’s Missile Programs
The development of missile technology in India began in earnest after the establishment of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP), initiated in 1983, marked a significant milestone in India’s quest for self-reliance in missile technology.
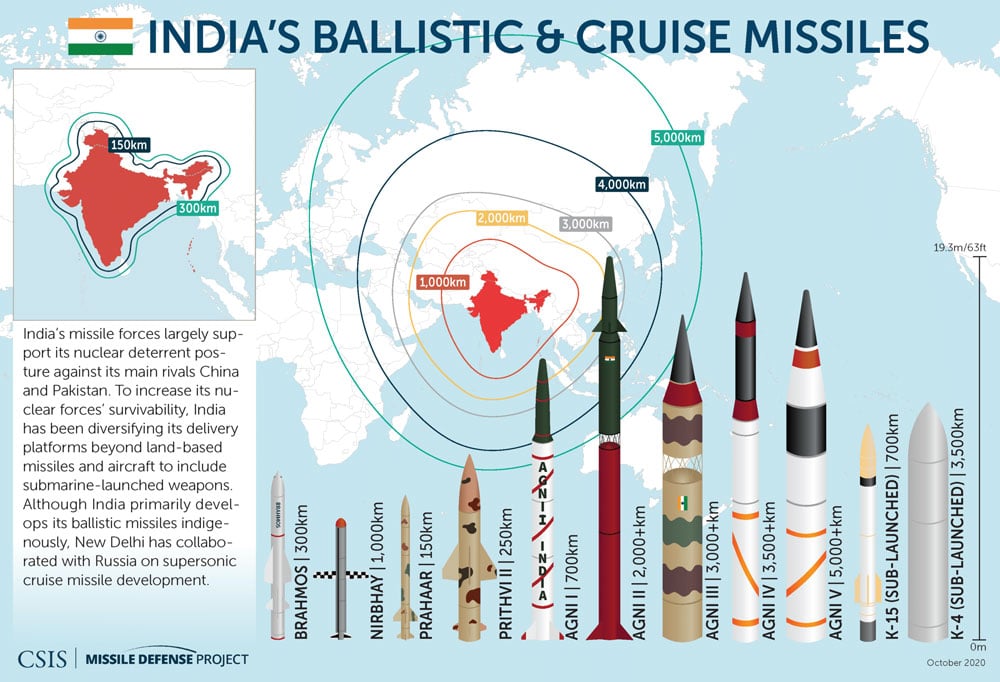
Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP)
The IGMDP aimed to develop a comprehensive range of missiles to meet the country’s defense needs. Key achievements of this program include:
- Prithvi: A short-range ballistic missile designed for tactical use.
- Agni: A series of intermediate to intercontinental ballistic missiles, enhancing India’s strategic deterrent capability.
- Akash: A medium-range surface-to-air missile that bolsters air defense.
Other Notable Programs
In addition to the IGMDP, India has pursued various other missile initiatives:
- BrahMos: A joint venture with Russia that has produced one of the world’s fastest cruise missiles, capable of being launched from land, sea, and air.
- Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD): This program aims to develop systems capable of intercepting incoming ballistic missiles, thereby enhancing national security.
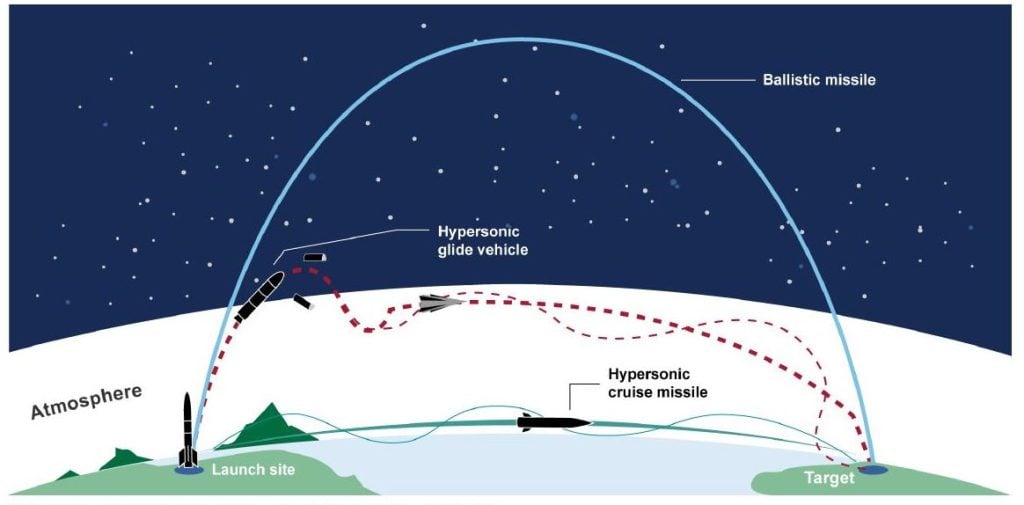
Classification of Missiles in India
India’s missile arsenal can be classified based on multiple criteria, including speed, trajectory, launch mode, and strategic importance.
Based on Speed
- Subsonic Missiles: Travel slower than the speed of sound (e.g., Prithvi).
- Supersonic Missiles: Exceed the speed of sound but are below Mach 5 (e.g., BrahMos).
- Hypersonic Missiles: Achieve speeds greater than Mach 5, with ongoing developments in this category.
Based on Trajectory
- Ballistic Missiles: Follow a parabolic trajectory and are powered during the initial phase (e.g., Agni series).
- Cruise Missiles: Fly within the atmosphere at a constant speed and can maneuver during flight (e.g., BrahMos).
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles: Achieve hypersonic speeds during re-entry (e.g., ongoing projects like the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle).
Types of Missiles Based on the Launch Mode
| Launch Mode | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Surface-to-Surface | Land-based platforms launching missiles at ground targets | Prithvi, Agni, BrahMos |
| Surface-to-Air | Land-based systems designed to counter aerial threats such as aircraft, helicopters, and drones | Akash, MRSAM |
| Air-to-Surface | Missiles launched from aircraft targeting ground-based assets | Helina anti-tank missile (from Rudra helicopter) |
| Air-to-Air | Aircraft deploying missiles against other aerial targets | Astra BVR air-to-air missile (from Tejas) |
| Ship-to-Ship | Naval vessels launching missiles at other ships or submarines | BrahMos anti-ship cruise missile (from naval ships) |
| Ship-to-Air | Naval ships equipped with missiles to defend against aerial threats | Barak-8 LR-SAM (on naval ships) |
| Submarine-launched | Missiles fired from submerged submarines | K-15 submarine-launched ballistic missile |
| Shoulder-fired | Portable missile systems operated by individual soldiers | FIM-92 Stinger, Igla shoulder-fired SAMs |
Strategic Importance of India’s Missile Capabilities
India’s missile systems play a vital role in establishing a credible deterrent and enhancing national security. The strategic significance can be categorized into two main areas: deterrence and tactical capability.
Deterrence
India’s long-range ballistic missiles, such as the Agni series, are integral to its nuclear deterrent strategy. These missiles ensure that India can respond effectively to nuclear threats, thereby maintaining stability in the region.
Tactical Capability
Tactical missiles like the Prithvi and BrahMos provide India with the ability to conduct precision strikes against key enemy assets, including military installations and logistics hubs. This capability is crucial for maintaining an edge in conventional warfare scenarios.

Challenges in Missile Development
Despite significant advancements, India faces several challenges in its missile development programs:
Dependence on Imports
India continues to rely on foreign imports for critical components, such as advanced sensors and propulsion systems. This dependence can hinder the development of a fully indigenous missile program.
Technological Hurdles
Many missile programs have encountered delays due to technological complexities. Ensuring timely development and deployment of missile systems is essential for maintaining strategic readiness.
Funding Constraints
Missile development is capital-intensive, requiring sustained funding to support research, development, and production. Attracting private investment and ensuring government support is crucial for the growth of this sector.
Future Prospects
The future of missile technology in India looks promising, with ongoing research and development in several areas:
Hypersonic Technologies
India is actively pursuing hypersonic missile technology, which promises to enhance strike capabilities significantly. Successful development in this area could provide India with a substantial strategic advantage.
Advanced Defense Systems
Enhancements in ballistic missile defense systems are also on the horizon. These systems aim to provide a robust shield against incoming threats, thereby increasing national security.
Collaboration and Innovation
Collaborative efforts with global defense partners can accelerate technological advancements. Engaging in joint ventures and sharing expertise will be vital for India to stay at the forefront of missile technology.
Conclusion
India’s missile capabilities are a testament to its commitment to national security and technological advancement. With a diverse arsenal that includes ballistic and cruise missiles, India is well-equipped to address contemporary security challenges. As the nation continues to innovate and develop its missile systems, it is poised to strengthen its position as a formidable military power in the region.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main types of missiles developed by India?
India has developed various missile systems, including ballistic missiles (Agni, Prithvi), cruise missiles (BrahMos, Nirbhay), and surface-to-air missiles (Akash, Barak).
Q2: How does India’s missile technology enhance its defence?
India’s missile technology provides a credible deterrent against potential adversaries, enhances tactical strike capabilities, and strengthens overall military readiness.
Q3: What is the significance of the Agni series?
The Agni series of missiles serves as India’s primary nuclear deterrent, with varying ranges that enable strategic reach across the Asia-Pacific region.
Q4: What challenges does India face in missile development?
India faces challenges such as dependence on imports for critical components, technological hurdles, and funding constraints that impact missile program timelines.
Q5: What are the future prospects for India’s missile technology?
Future prospects include advancements in hypersonic technologies, enhanced ballistic missile defence systems, and increased collaboration with global defence partners.


















