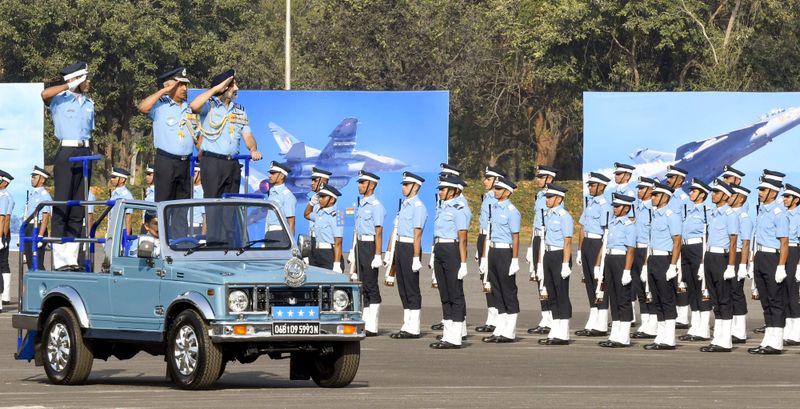
In a significant step for the Indian Air Force (IAF), the inaugural group of officers from the newly established Weapon Systems Branch graduated from the Air Force Academy (AFA) in Dundigal, near Hyderabad. This milestone event took place on Saturday as part of the Combined Graduation Parade, which saw 204 cadets, including 26 women, commissioned as flying officers. The ceremony was presided over by the Chief of the Air Staff, Air Chief Marshal AP Singh.
The creation of the Weapon Systems Branch marks a historic development within the IAF, representing the first new operational branch established since India’s independence. The initiative aims to unify all weapon system operators across various ground-based systems and airborne platforms under a single operational stream. During the Air Force Day celebrations in Chandigarh in 2022, then Chief of Air Staff Air Chief Marshal Vivek Ram Choudhari outlined the objectives of this new branch, emphasizing its focus on managing four specialized streams: surface-to-surface missiles, surface-to-air missiles, remotely piloted aircraft, and weapon system operators in multi-crew aircraft. Choudhari had noted that this strategic move would lead to a savings of over Rs 3,400 crore due to reduced expenditures on flying training.
The training program for weapon system operators has been meticulously structured into two stages. The first phase takes place at the AFA, followed by advanced specialized training at the newly established Weapon Systems School located at Begumpet, near Hyderabad. This training is designed to equip the officers with the necessary skills to proficiently operate a variety of complex weapon systems.
The newly formed branch is further divided into four sub-streams, each focusing on different operational capabilities. The first sub-stream, ‘Flying,’ involves weapon system operators functioning in aircraft such as the Su-30MKI, AH-64E Apache attack helicopters, Soviet-origin Mi-25/35, indigenous Prachand helicopters, and special operations aircraft including the C-130J Super Hercules.
The second sub-stream, ‘Remote,’ concentrates on the operation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) or drones, which have become crucial for a range of military missions including attack, surveillance, and logistical support. Some of these UAVs are procured from international suppliers like the United States and Israel, while others are developed and manufactured domestically.
The third sub-stream is ‘Intelligence,’ involving the interpretation of imagery gathered from various surveillance assets, including space systems, manned aircraft, and UAVs. This section also encompasses intelligence analysts and specialists in information warfare, as well as operators responsible for collating signals intelligence.
Completing the structure is the fourth sub-stream, ‘Surface,’ which includes commanders and operators of surface-to-air guided weapons and surface-to-surface systems. This category encompasses operations involving advanced missile systems like the Akash, as well as ballistic and cruise missiles including the Prithvi and BrahMos.
During the graduation parade, Air Chief Marshal Singh highlighted the rapidly evolving nature of warfare and the necessity for adaptability in aerospace operations. He emphasized the importance of collaboration among branches of service and the pivotal role each officer plays in successful mission execution.
Recognition was given to the outstanding performance of the cadets, with Flying Officer Parag Dhankar receiving the President’s Plaque and the Chief of the Air Staff Sword of Honour for his exemplary achievements in the pilots’ course. Meanwhile, Flying Officer Ram Prasad Gurjar was honored with the President’s Plaque for securing first place in the ground duty stream. The commissioning of these officers into the Weapon Systems Branch marks a progressive stride for the IAF, fortifying its operational capabilities in an ever-evolving defense landscape.