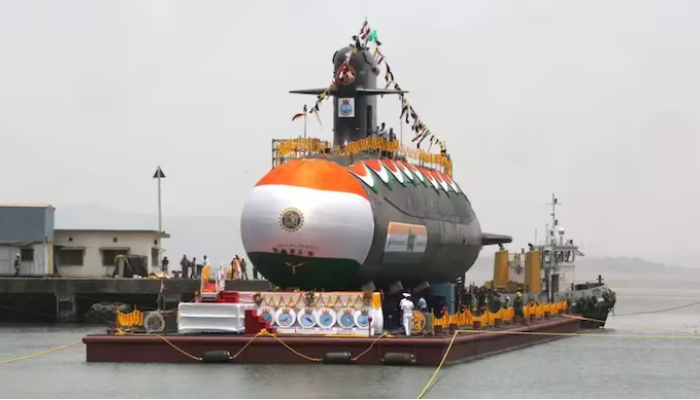
In a significant advancement for India’s defense capabilities, the newly commissioned nuclear-powered submarine INS Arighaat has successfully conducted a test of the country’s nuclear-capable K-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM). The test took place in the Bay of Bengal on November 27, off the coast of Visakhapatnam.
The INS Arighaat, which weighs 6,000 tons, launched the solid-fueled K-4 missile, boasting an impressive range of 3,500 kilometers. Although there was no formal announcement about the missile test, sources within the defense establishment confirmed that it was indeed carried out from this advanced submarine.
Defense sources revealed, “The test of the ballistic missile was done for the full range. The details are being analysed and the top military and political brass would be briefed by officials concerned on the exact details after complete analysis.” This marked the first occasion that the K-4 missile has been launched from the INS Arighaat, underscoring India’s ongoing efforts to enhance its long-range missile capabilities.
In recent years, submersible pontoons were the primary platforms utilized for testing the K-4. The analysis of the test results will determine whether the missile launch met the established trial objectives and specifications. The successful launch represents a crucial step in bolstering India’s sea-based nuclear deterrence.
This test was conducted within a previously established flight corridor in the Bay of Bengal between November 27 and November 30, which had been communicated through a public area warning. The INS Arighaat, commissioned into the Indian Navy in August, is the nation’s second nuclear-powered submarine designed to carry nuclear-tipped ballistic missiles, known in naval terminology as SSBNs.
Differentiating itself from its predecessor, the INS Arihant, which is equipped with K-15 missiles with a range of 750 kilometers, the INS Arighaat’s capability to carry the K-4 missile enhances India’s strategic deterrence. The country also plans to launch its third SSBN, the INS Aridhaman, which will have a displacement of 7,000 tons, in the near future.
Recently, the Indian Cabinet Committee on Security approved the construction of two additional nuclear-powered attack submarines, indicating India’s commitment to strengthening its naval presence and strategic influence, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region.
The K-4 missile, developed by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), is an essential component of India’s military arsenal, aimed at equipping its nuclear submarines for effective deterrence. Currently, several countries, including the United States, Russia, and China, maintain SLBMs with ranges exceeding 5,000 kilometers, making India’s advancements in this area even more critical for its national security strategy.