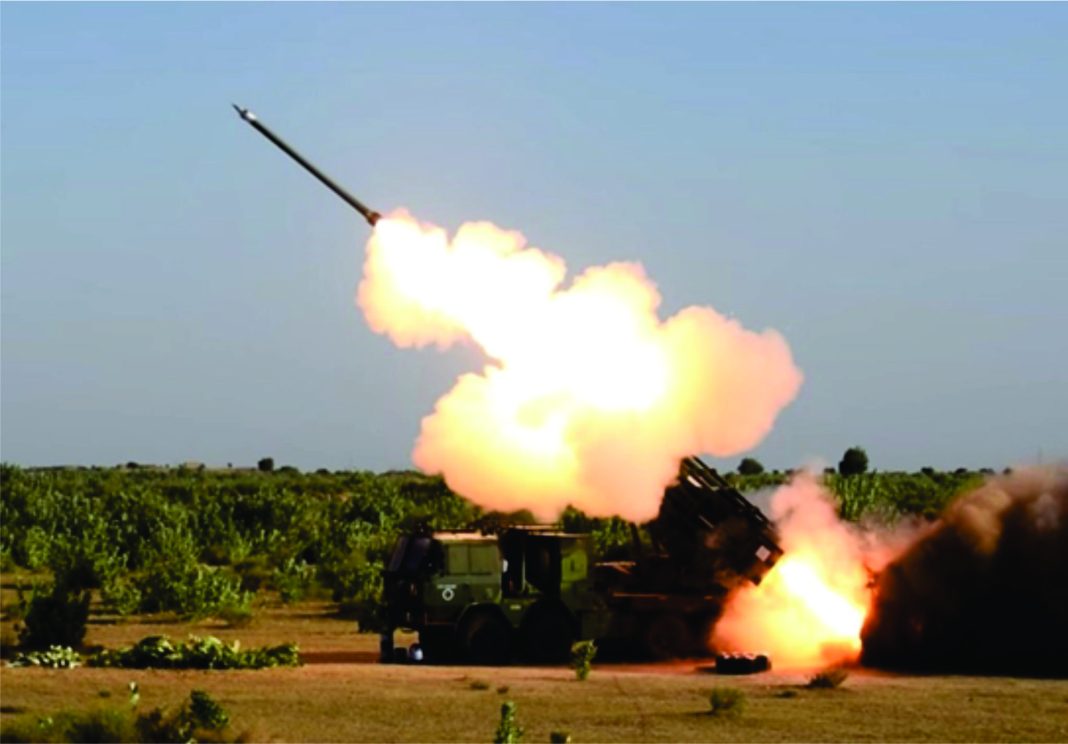
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted flight testing of the Guided Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL), marking a significant advancement in the country’s artillery capabilities. The comprehensive three-phase test aimed to evaluate the system across multiple parameters, including range, accuracy, consistency, and the rate of fire for engaging multiple targets in a salvo mode.
As part of the testing process, the initiative involved launching 12 rockets from each production agency using a pair of in-service Pinaka launchers, as confirmed in a statement released by the Indian Ministry of Defence.
The Guided Pinaka, a precision strike variant designed and developed by the Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE), showcases the capability to effectively strike targets located up to 75 kilometers (approximately 47 miles) away. The system operates with a configuration that includes 18 launchers, each equipped with 12 launch tubes, mounted on a robust 8×8 Tata vehicle.
The original iteration of the Pinaka MBRL had a range of 37.5 kilometers (23.3 miles) and an accuracy requirement of within 500 meters (1,640 feet). However, a significant upgrade was accomplished in 2016 when a guidance kit was integrated into the system. This enhancement not only extended its range but also drastically improved accuracy to within 10 meters (33 feet), making it a formidable asset on the battlefield.
In addition to the recent successful flight tests, earlier this year, two new variants of the Pinaka were approved for development with impressive engagement ranges of 120 kilometers (74 miles) and 300 kilometers (186 miles). These advancements are expected to bolster India’s artillery capabilities and enhance its preparedness for various operational scenarios. The successful testing of the Guided Pinaka aligns with the ongoing efforts of the Indian military to modernize its defense systems and respond to evolving security challenges in the region.