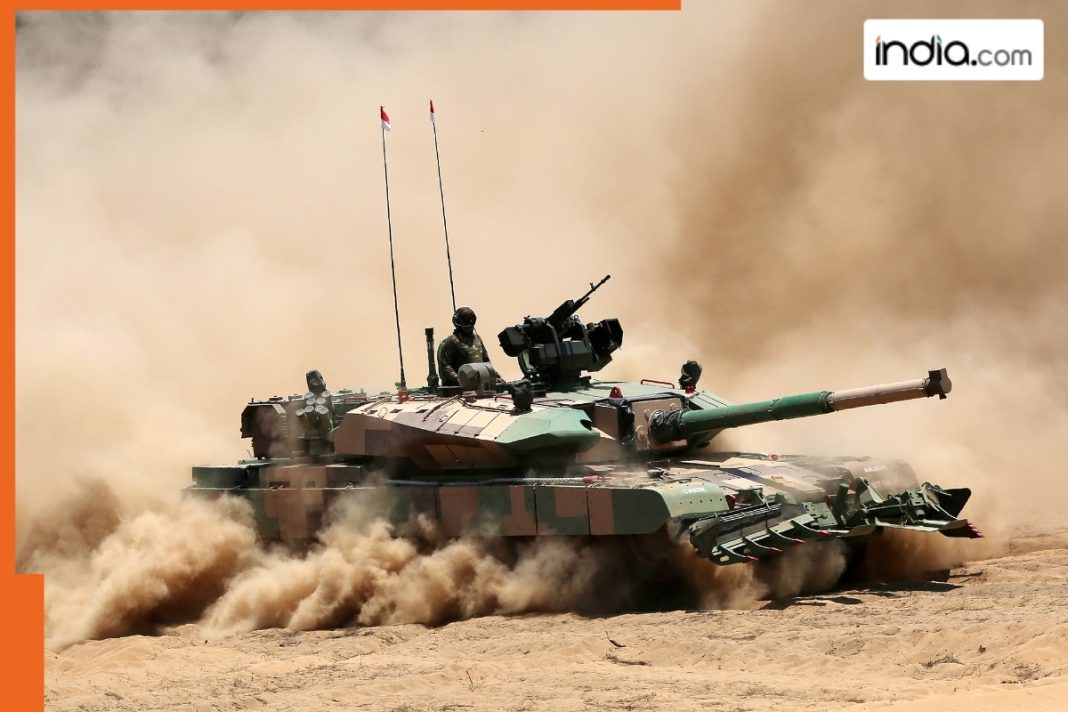
In a significant development for India’s defense capabilities, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is advancing its efforts in manufacturing smoothbore guns for the Next Generation Main Battle Tank (NGMBT), also known as the Future Main Battle Tank (FMBT). This initiative is part of a broader strategy to modernize the Indian Army’s arsenal and maintain a competitive edge over regional adversaries, particularly Pakistan and China.
The NGMBT, which embodies the evolution of India’s tank technology, is designed to be considerably lighter and more advanced than its predecessor, the Arjun Mk1. It incorporates cutting-edge features such as advanced electro-optical sight systems and the potential for a high power laser-based weapon system, alongside its primary gun.
DRDO is currently focusing its efforts on developing two key smoothbore gun systems with calibers of 120mm and 125mm. Smoothbore guns, which lack the rifling found in traditional barrels, enable tanks to launch various projectiles, including guided missiles, from the same barrel. This dual-use capacity enhances the versatility and strike capability of modern tanks, making them more adaptable to different combat scenarios.
The decision to develop a 120mm caliber gun for the Future Ready Combat Vehicle (FRCV) highlights India’s commitment to indigenous defense manufacturing, while the 125mm caliber gun is favored for its stronger firepower and compatibility with munitions readily available in the global market. This focus on multiple calibers is aimed at providing the Indian Armed Forces with greater flexibility in terms of weapon selection and operational readiness.
The smoothbore design offers practical advantages: it simplifies the firing mechanism, allowing for faster reloading and increased rate of fire. However, it is essential to note that the overall firing range of these tanks is influenced by numerous factors, including environmental conditions and the type of ammunition used.
India’s push to enhance its defense infrastructure comes at a critical time when geopolitical tensions in the region necessitate a strong and modern military. The advancements in tank technology not only bolster the operational capabilities of the Indian Army but also serve as a counterbalance to the evolving military capabilities of neighboring countries. As DRDO continues its development work, the implications for regional security dynamics are likely to be significant, raising concerns in Islamabad and Beijing regarding the balance of power in South Asia.