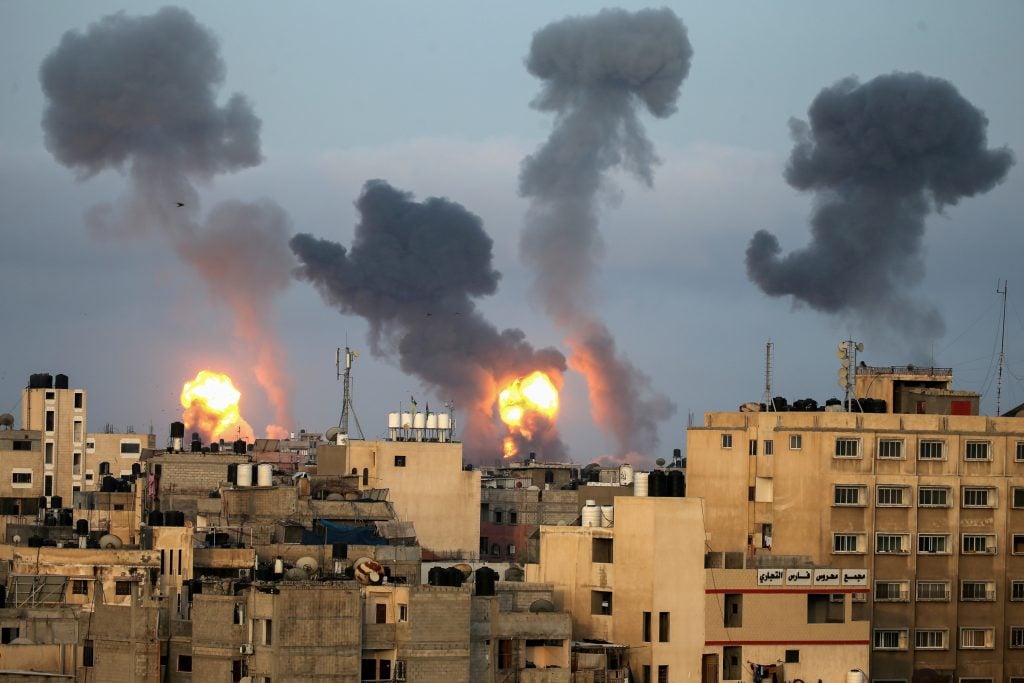
Israel Palestine SSB Interview Questions: The Israel-Palestine conflict is one of the most intricate and long-standing geopolitical disputes in modern history. With its roots stretching back over a century, the issue has evolved to encompass various facets, actors, and turning points. One key player in this conflict is Hamas, the Palestinian organization that emerged in the late 20th century. For defence aspirants preparing for the SSB Interview, a sound understanding of this conflict is vital. This article aims to shed light on the current situation, followed by potential questions you might encounter during the interview.

Potential SSB Interview Questions:
- Historical Understanding:
- Can you briefly explain the origins of the Israel-Palestine conflict?
- Who are the primary stakeholders in this conflict, and what are their objectives?
- Current Events:
- What were the recent triggers that escalated tensions between Israel and Palestine?
- How has the role of Hamas evolved over the years, and what is its current stance in the conflict?
- India’s Position:
- How has India’s stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict evolved over the years?
- In your opinion, should India take a more active role in mediating or resolving the conflict? Why or why not?
- Strategic and Defence Implications:
- How do global superpowers view the Israel-Palestine conflict, and why is it of strategic importance to them?
- Can there be a military solution to the Israel-Palestine issue?
- Ethical and Moral Dimensions:
- The conflict often involves civilian casualties. How do you think nations should approach the principle of proportionality in warfare?
- How do you view the ethical dimensions of asymmetrical warfare, as seen in the conflict between a well-equipped military and a militant organization?
- Potential Solutions:
- What could be the potential long-term solutions to this conflict?
- How important is the role of international mediation and organizations in resolving this issue?

Israel Palestine SSB Interview Questions
1. Q: What are the roots of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
A: The roots can be traced back to competing national movements: Zionism and Palestinian nationalism. Overlapping territorial claims in historic Palestine, the Balfour Declaration, British Mandate policies, and the influx of Jewish immigrants, led to tensions between Jewish and Arab communities. The 1948 Arab-Israeli war and subsequent wars further entrenched positions.
2. Q: What is the significance of the Balfour Declaration?
A: Issued in 1917, it was a letter from the British Foreign Secretary, expressing support for the establishment of a “national home for the Jewish people” in Palestine, without prejudicing the rights of existing non-Jewish communities. This was seen by Jews as backing for a Jewish homeland and by Palestinians as disregarding their national rights.
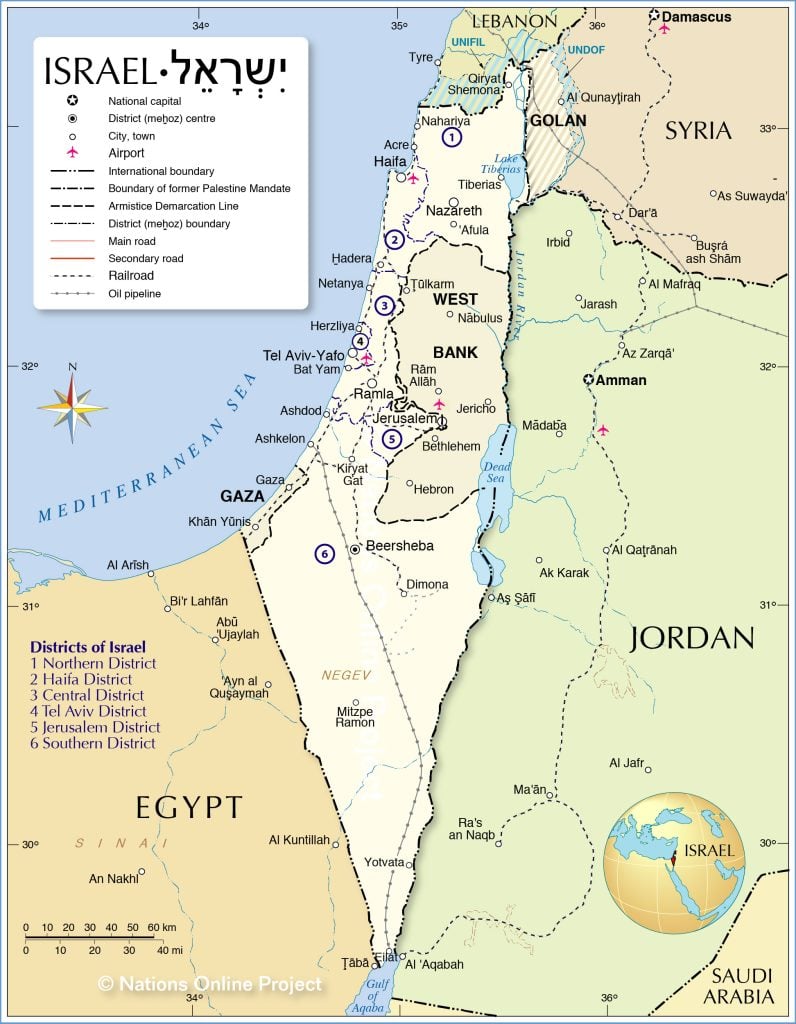
3. Q: How did the 1948 war affect the Palestinian population?
A: The 1948 war, or the Nakba (catastrophe) as referred to by Palestinians, led to the displacement of around 700,000 Palestinians. Many became refugees in neighboring countries or in the West Bank and Gaza.
4. Q: What are the Oslo Accords?
A: Signed in the early 1990s, the accords are a series of agreements between Israel and the PLO, aiming to achieve a two-state solution. They established the Palestinian Authority and provided for limited self-governance in certain territories.
5. Q: Why is Jerusalem so contentious?
A: Jerusalem is sacred to Jews, Muslims, and Christians. While Israel considers it its undivided capital, Palestinians regard East Jerusalem, which was occupied by Israel in 1967, as the capital of a future state.
6. Q: How do settlements impact the conflict?
A: Jewish settlements in the West Bank are considered illegal under international law. Their expansion complicates the feasibility of a contiguous Palestinian state and exacerbates tensions.
7. Q: What’s the significance of the 1967 Six-Day War?
A: Israel captured the West Bank, Gaza, East Jerusalem, Sinai, and the Golan Heights. The war set the stage for the occupation of Palestinian territories, which continues to this day.
8. Q: How does Hamas differ from the Palestinian Authority (PA)?
A: The PA is secular and recognizes Israel, whereas Hamas, an Islamist group, originally did not recognize Israel’s right to exist and has been in conflict with it. The PA governs the West Bank, and Hamas governs Gaza.
9. Q: What are the main points of contention in peace negotiations?
A: Major issues include the status of Jerusalem, borders, settlements, refugees, security arrangements, and mutual recognition.
10. Q: How do other Middle Eastern countries influence the conflict?
A: Neighboring countries have historically been involved, either directly in wars or through diplomatic and financial support. The geopolitics of the region, including rivalries and alliances, influence the dynamics of the conflict.





Vudesh