RBBB – Right Bundle Branch Block: In the AFSB medical test one of the problems less known to the candidates is the RBBB. As much as 40% of the candidates appearing for the medical test are found to have this problem. This could be a reason for rejection. But the good news is that you are given a chance to prove that this problem does not affect your performance. First let us know what this actually means.
A right bundle branch block (RBBB) is a defect in the heart’s electrical conduction system. During a right bundle branch block, the right ventricle is not directly activated by impulses travelling through the right bundle branch. The left ventricle however, is still normally activated by the left bundle branch. These impulses are then able to travel through the myocardium of the left ventricle to the right ventricle and depolarise the right ventricle this way. As conduction through the myocardium is slower than conduction through the Bundle of His-Purkinje fibres, the QRS complex is seen to be widened. The QRS complex often shows an extra deflection which reflects the rapid depolarisation of the left ventricle followed by the slower depolarisation of the right ventricle.
RBBB usually has pathological cause, although it is seen in healthy individuals.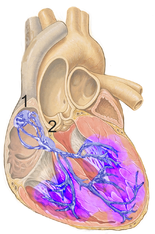
Normal electrical conduction system of the heart (Schematic). All myocardial segments are excited almost simultaneously (purple staining).
1. Sinoatrial node
2. Atrioventricular node.
Conduction in RBBB (Schematic): With a blockage in the right bundle branch (red), the left ventricle is excited in time (purple), while the excitation of the right ventricle takes a detour via the left bundle branch (blue arrows).
|
 * *
ECG characteristics of a typical RBBB showing wide QRS complexes with a terminal R wave in lead V1 and slurred S wave in lead V6. |
Clinical test: This problem is diagnosed during the clinical test done by the examining medical officer. Initially he checks by placing his palm on the chest and abdomen of the candidate. The candidate is asked to breathe deeply, shallowly and hold his breath as told so by the officer. Then the same is tested with a stethoscope. At this point if he gets a hint of RBBB then the candidate has to undergo 2 tests viz.
2D – Echo
The 2D – Echo is done by the clinical officer himself. This is a test where an electrode is placed on the chest part of the candidate and the live action of his heart pumping is visualized on the computer screen. The officer checks for the valve opening and closing in the auricle and ventricle. At certain points he freezes the frame so as to record the readings at systole and diastole. This takes about hardly 10 minutes for each candidate. He could conclude the test as normal or otherwise at the end of the 10 minutes.
TMT – Tread Mill Test
This is a stress test. The basic idea of the test is to make your heart beat at its maximum capacity and see if it can polarize and depolarize without any issues at that high rate. This test requires great stamina. The candidate is connected with 8 electrodes to his chest which will record his ECG during the test. The arm band is tied around the biceps to record the BP. First the candidate is in the sleeping position when his readings such as BP, Heart rate and ECG are recorded and tabulated. The readings are once again noted while the candidate is in the standing position on the treadmill. Once that is done the treadmill starts moving.
Every 3 minutes on the treadmill is called a stage. Each stage is characterized by constant speed and constant slope of the machine. At the end of 3 minutes the next stage starts in which the speed increases and the inclination of the treadmill also increases. As the stage progresses you will feel like climbing up a mountain with steadily increasing your pace. During each stage the vital measurements are recorded by the system. As you run you will be able to see your readings just in front of you. The decision of stopping the test is with you. You can say the attending person if you think you cannot continue anymore. Usually stage 5 is the maximum achievable.
When to stop?
A simple indicator to know that you have run enough before stopping the test is to look for the BPM(Beats Per Minute) counter on the screen. The BPM column will be on the top right hand side of the screen. It shows the BPM as a number and just below it you will find % value. This percentage is nothing but the indication of what capacity of the heart’s beat has been reached. See to that you cross 90% before asking to stop the test.
 Author: Santhosh Kumar:
Author: Santhosh Kumar: He has cleared AFSB interview for technical branch, he has beautifully shared his AFSB interview experience in his blog ,
do check it here.

















I applied for SSC….and m a medical student….I had fracture of left hand 1 year ago…for which i was operated …now my movements are in full range…will they select me?
i am having a injury on my wrist and i am having medical test afte 2 days…. will they reject me?
Very true, we all do such great detailed researches and are least of any knowledge about the medicals. Thanks for sharing. Good to know.