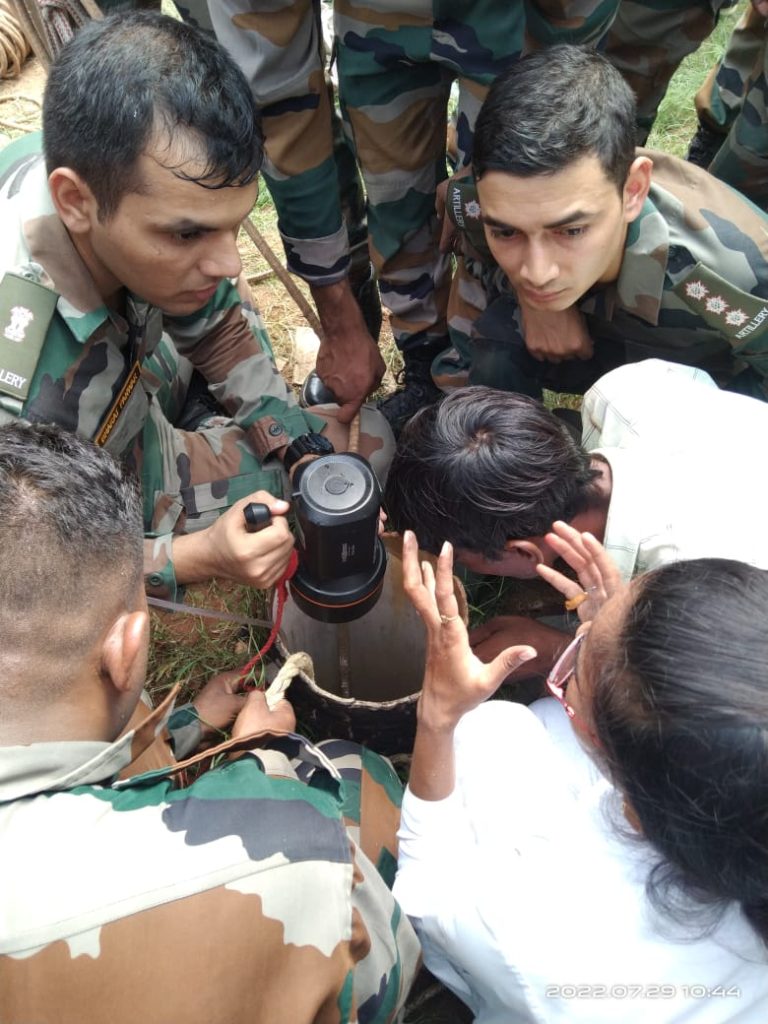
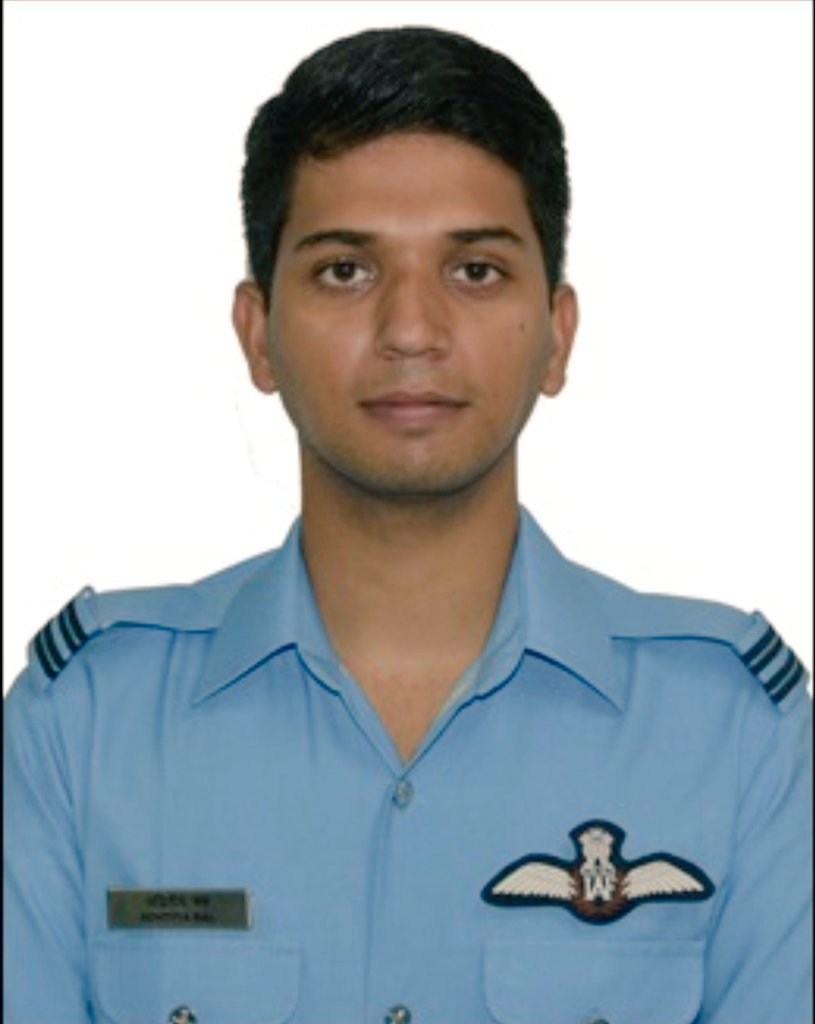
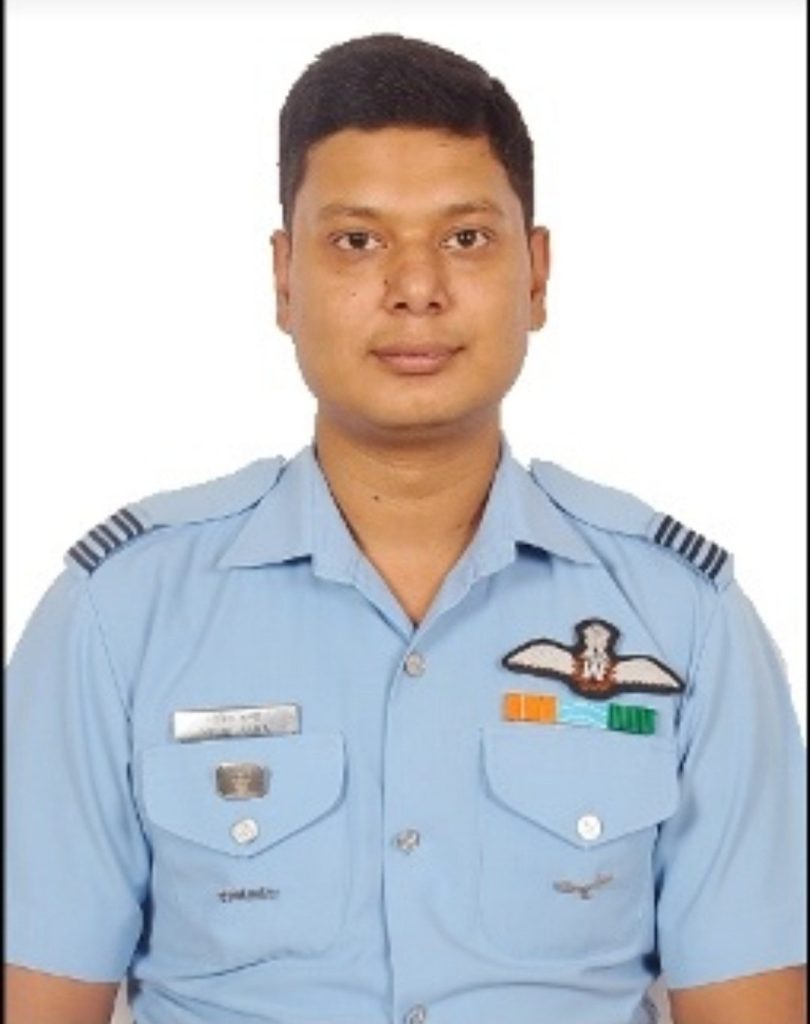
Another Mig-21 fighter plane crashed and we again lost brave warriors in the crash. The two pilots who lost their lives in the MiG-21 fighter aircraft crash in Barmer, Rajasthan last evening have been identified as Wing Commander M Rana and Flight Lieutenant Advitiya Bal.
The standard way of getting away from all the responsibilities will be followed and a court of enquiry will be set up to look into the incident and after few years the reports would come out either blaming the pilot’s incompetence or the technical faults. But one question has always been asked and will continue till the time this problem is solved, and the question is how many more crashes do we need to decommission the Mig-21 AKA ‘the flying coffins‘.
The infamous name ‘flying coffins’ or the ‘widow
maker’ was given to these planes because of the lives these planes have claimed
and that too in normal sorties and training missions, leave the combat and
dogfights scenario. This year this is the third crash of a Mig-21 and the total
death toll comprising both pilots and civilians is more than 200.
Also Read: Indian Air Force to retire all 4 MiG-21 squadrons by 2025
The question which arises is why do these planes
crash so frequently and if they are so infamous why does the Indian Air Force
still uses them.
Let’s try to find the answers to these questions.
So, What is MIG-21s?
“The MIG-21s are Single engine, single seater
multirole fighter/ground attack aircraft of Russian origin which forms the
back-bone of the IAF. It has a max speed of 2230 km/hr (Mach 2.1) and carries
one 23mm twin barrel cannon with four R-60 close combat missiles.” This is
the detail given on the IAF page but let’s dig in further to find out more
about the planes.
India opted to go for the Mig-21s in 1961 leaving
other western competitors. India was given all the rights on technologies and
also the rights for local assembly and production.
In 1964, the MIG-21 was inducted in IAF as the first supersonic jet of the fleet. The first experience is gained was in the Indo-Pak war of 1965 as a defensive interceptor and after the positive reviews from several Air force pilots, the number of orders and production was increased. They also demonstrated excellent fighting skills in the 1971 war and were modernised and configured more according to the needs of the Indian Air Force.
The recent operational success of the MIG-21 is the dogfight that happened in Jammu and Kashmir after the Balakot Air Strike in the year 2019. A Pakistani Air Force F-16 was shot down by Wing Commander Abhinandan Varthman, although we also lost our MIG, fighting an advanced generation aircraft and shooting it down is a success in itself.
What causes the frequent MiG 21 crash?
The causes can be broadly divided into three parts :
- Fault in design
- Age of the machine
- Purchase of faulty second-hand parts
1. Fault in design: The experts claim that one of the major reason for frequent crashes is a major lag in the design of the machine and that is during the operations when in afterburner, the engine operates very close to its surge line and the ingestion of even a small bird can lead to an engine surge/seizure and flame out.
The other notable faults in design include :
A. Low Aspect Ratio: The low aspect ratio of 2:2 requires more precision while manoeuvring as compared to other fighter pilots.
B. Approach Speed: With increase in weight, the approach speed also needs to increased but the power delivery of MIGs is not that great and is further decreased when it comes to Indian Scenario and climatic conditions.
C. Problems during Emergency : In a MiG the pilot has to push the stick forward, build up his energy and then after a delay of several seconds, pull back the stick to climb away. He may simply not have the time when flying close to the ground.
D. Ejection Seat : The CK ejection seat used in MIG’s is good for high altitudes but definitely not good for lower altitudes as it increases the ejection time, leading to failure of many low level ejections.
2. Age of the machine: Although the planes demonstrated great success in the 1971 war later on after modernisation in all the Air forces of the world and due to the increasing age of the planes IAF decided to decommission them in a phased manner since the 1980s, although the MIG-21 FL was decommissioned in the year 2013 after 50 years of service the MIG-21 Bison are still in operations, and when the age is this much you can’t expect the old ladies to outperform the enemies.
3. Faulty second-hand spare parts: Russia
had stopped the production of these aircraft and their parts long back and to
keep the MIG’s operational we need spare parts which we purchase in second
hands from Israel and Ukraine. Moscow has warned consistently about purchasing
such parts and using them in the planes and claims that these are also the
causes of such crashes.
Views on the crash: There
are differing views regarding the crashes even among the officers of the Indian
Air Force, some leaders claim that is a criminal act of negligence by the
political leaderships that the 60 years old planes are still being used.
The other view is that the number of crashes of MIG-21’s gets this amplification because the number of these fighter jets in the fleets is too high.
Air Chief Marshal (retd.) P.V. Naik, the former
chief of the Indian Air Force, told The New York Times – “I have flown more
than 2,000 hours in various variants of the MIG-21. Any issue with the MIG-21
gets magnified because much of the fleet comprises of this type.”
Why has the Indian Air Force still not
switched over?
The decision to decommission the MIG-21s in a phased manner was initiated in the early 1980s and a new project, TEJAS was to be launched in place of the MIG’s but thanks to the Red tape system of India, the decision making took such a long time and the plan of inducting and developing new planes was delayed.
The reason for operating MIG’s even today is the
non-availability of other fighter jets, If all the MIG’s are decommissioned
from the immediate effects we will have a serious void in the numbers of
fighter jets owned by our country, which can lead to threat in secured
airfields.
The then Air Vice Marshall SJ Nanodkar told The
Tribune in the year 2017– “The IAF is compelled to carry on using the
MiG-21 in the absence of a viable option. This will continue as no immediate
replacements are coming.”
The IAF is
demanding new planes for 2 decades and the recent induction of Rafaels and
TEJAS – LCA’s is the silver lining in the cloud but we need to increase the
numbers of the planes rapidly with invested innovations, and this needs to be
done urgently if we don’t want to lose our brave warriors and leave everything
at the sake of a court of enquiry.
Air Marshal (retd) Anil Chopra said in an interview “Even
smaller air forces retired MiG-21s long ago. Every crash of an old aircraft is
a reminder for IAF to replace older fleets. Modernisation of IAF is behind
schedule. Two things are needed immediately. Accelerate the development of LCA
variants, increase their rates of production and speed up the advanced medium
combat aircraft (AMCA) project. Secondly, send out the request for proposal for
114 new fighters,”
The numbers of new fighter planes can be increased
by setting up efficient production lines in a public-private partnership model
and ensuring that options of technology transfer are also considered.

The Modernization plans:
IAF is going to induct variants of LCA Tejas to replace the ageing MIG-21 and a budget of Rs. 48,000 crore was awarded by the defence ministry to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited in February 2021, for 83 LCA Mk-1A jets for IAF.
The supply time is estimated to be around 2030 for the supply of 73 Mk-1A fighter Jets and 10 LCA Mk-1 trainer aircraft. 40 LCA’s are undergoing initial operational clearance (IOC) and final operational clearance (FOC) configurations and will be the most advanced variant of Tejas, but we need to increase the speed of these modernizations.