Sniper rifles have always played a crucial role in military and law enforcement operations. These precision weapons are designed to deliver accurate and lethal shots at long distances, making them essential tools for snipers on the field. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of sniper rifles and highlight the best options available today.

Whether you’re a military professional, a law enforcement officer, or an avid shooting enthusiast, this article will provide you with valuable insights and help you make an informed decision when it comes to choosing the best sniper rifle for your needs.
The Evolution of Sniper Rifles
Sniper rifles have come a long way since their inception. Over the years, advancements in technology and design have led to the development of highly capable and versatile sniper rifles. Today, sniper rifles are more accurate, reliable, and adaptable than ever before. Let’s take a journey through the evolution of sniper rifles and explore the key milestones that have shaped their development.

The Golden Age of the Long Gun
In the last two decades, there have been significant advancements in rifle manufacturing, optics, and ammunition. These advancements have revolutionized the capabilities of sniper rifles and led to the emergence of more precise and versatile long-range weapons. The integration of electronics into optics and ballistic support systems, combined with the availability of high-quality bullets and ammunition, has contributed to the golden age of the long gun.
Classic Sniper Rifles
Some classic sniper rifle platforms have stood the test of time and continue to be reliable choices for snipers. The USMC M40 and the Soviet-Era SVD are prime examples of such platforms. These rifles have been in service for more than half a century and have proven their effectiveness on the battlefield.
Newer Sniper Rifle Systems
In addition to the classic platforms, several newer sniper rifle systems have quickly gained popularity and established good reputations. These rifles offer advanced features and capabilities that make them well-suited for modern sniper missions. Let’s take a closer look at some of the best sniper rifles currently in use.
Best Sniper Rifles Currently In Use
When it comes to selecting the best sniper rifle, several criteria come into play. We have carefully considered factors such as track record, commercial availability, and the spectrum of missions covered to compile this list of the best sniper rifles currently in use. These rifles have been extensively field-tested and have proven their effectiveness in various operational environments. Let’s delve into the details of each rifle.
Accuracy International AXSR
The Accuracy International AXSR is widely regarded as one of the best sniper rifles in the world. It boasts unparalleled toughness, innovation, and accuracy, carrying on the legacy of Accuracy International’s renowned sniper rifles. The AXSR features a multi-caliber design, allowing for quick conversion between different cartridges. It incorporates AI’s signature flat-bottomed, six-lug magnum-length action and their newest chassis. The rifle’s ruggedness and accuracy have been demonstrated in extreme long-range matches, making it an excellent choice for snipers who require precision and reliability.

Accuracy International AT308
The Accuracy International AT308 is the little brother of the AXSR and a favorite among police snipers. This short-action rifle chambered in .308 Win. offers various configuration options, including barrel lengths, folding stock, and different finishes. The base model, equipped with proven features such as AI’s flat-bottomed, six-lug action and their own two-stage trigger, is reliable and affordable. The AT308’s accuracy and performance have been tested in challenging shooting scenarios, making it one of the best sniper rifles for engagements up to 1,000 yards.

Barrett Mk22 MRAD
The Barrett Mk22 MRAD is a modular switch-caliber rifle that stands out among the best sniper rifles in the U.S. military arsenal. It can easily switch barrels and cartridges while maintaining excellent accuracy. The Mk22 won the U.S. Special Operations Command’s Advanced Sniper Rifle (ASR) trial, showcasing its precision and multi-caliber capability. The rifle comes with barrels in different calibers, such as 7.62×51 NATO (.308 Win.), .300 Norma Mag., and .338 Norma Mag. Its ability to consistently deliver tight groups at extended ranges makes it a popular choice among long-range shooters.

Mk 13 Mod 0/5/7
The Mk 13 sniper rifle has become synonymous with the Navy SEALs and is considered one of the best sniper rifles in the world. It is a modified Remington 700 long action paired with an Accuracy International AICS or McMillan A2 stock. The Mk 13, chambered in .300 Win. Mag., has an official effective range of 1,200 yards but can achieve longer shots. Its accuracy has been demonstrated by renowned snipers like Chris Kyle, who achieved a verified kill at 1,600 yards using the Mk 13. The rifle’s iconic look and exceptional performance make it a top choice among elite snipers.

Barrett M82/M107
The Barrett M82/M107 is a legendary semi-automatic .50-caliber sniper rifle known for its immense power and ability to penetrate various targets. While it may lack pinpoint accuracy compared to other sniper rifles, its primary role is anti-material engagement. The M82/M107 is widely used for disabling vehicles, destroying lightly armored targets, and neutralizing threats behind cover. Its recoil management system effectively reduces felt recoil, allowing for accurate follow-up shots. The M82/M107’s reputation and proven performance have solidified its place as one of the best sniper rifles ever created.
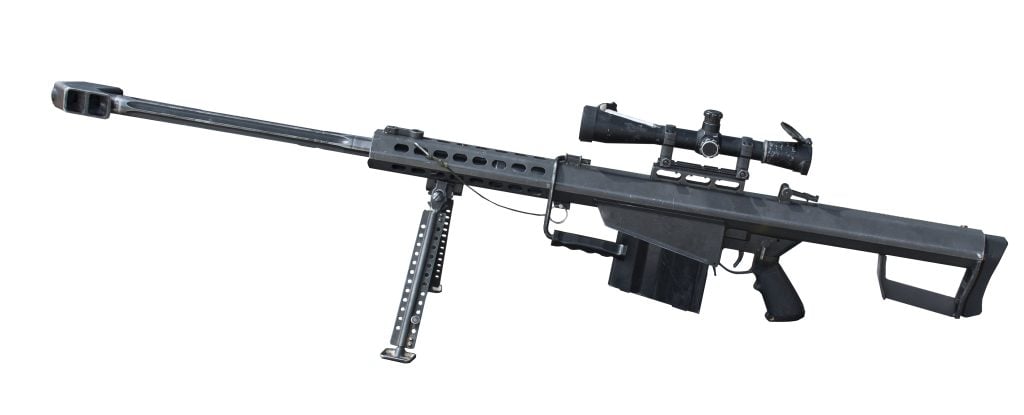

USMC M40
The USMC M40 is a true classic and one of the oldest sniper rifles on this list. It has been in service since 1966 and has undergone several iterations to meet the evolving needs of Marine Scout/Snipers. The M40 is built on a Remington 700/40X bolt action and features a rugged stock designed for combat conditions. It has proven its reliability and accuracy over the years, earning the respect and loyalty of Marine snipers. The M40’s simplicity and effectiveness make it a timeless choice for those seeking a reliable sniper rifle.

M24 Sniper Weapon System (SWS)
The M24 Sniper Weapon System is the primary sniper rifle used by the U.S. Army. Based on the Remington 700 platform, the M24 is a bolt-action rifle chambered in .308 Win. It offers exceptional accuracy and reliability, making it a trusted companion for Army snipers. The M24 has undergone various upgrades over the years, including improved stocks, detachable magazines, and the ability to mount sound suppressors. Its long-standing service and reputation as a formidable sniper rifle have made it a staple in the U.S. Army’s arsenal.

Sako TRG M10
The Sako TRG M10 is a highly innovative sniper rifle that deserves more recognition. Although it was the runner-up in the PSR trials, it is considered by many experts to be superior to the Remington MSR Mk 21. The TRG M10 features a quick-barrel change system and a chassis stock with exceptional ergonomics. Its adjustable length of pull and cheek height, along with an integrated tool kit, make it a versatile and user-friendly rifle. The TRG M10’s accuracy and durability have been highly praised by those who have had the opportunity to shoot it.

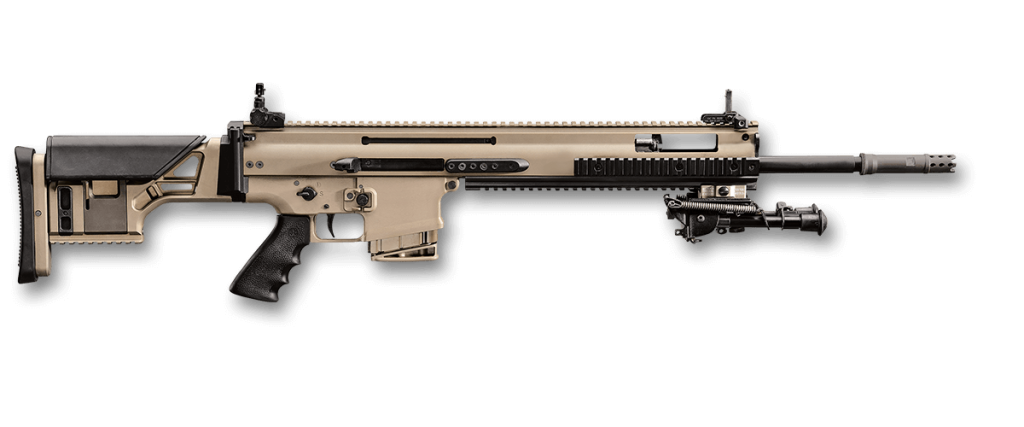
FN SCAR Mk 20 SSR
The FN SCAR Mk 20 SSR is a semi-automatic sniper rifle chambered in 7.62×51 NATO (.308 Win.). It combines the reliability and versatility of the FN SCAR platform with enhanced accuracy for long-range engagements. The Mk 20 SSR features a longer trunnion for improved barrel support and a quad rail configuration for accessory attachment. Its ambidextrous controls and adjustable stock make it suitable for a wide range of shooters. While not as well-known as some other sniper rifles, the Mk 20 SSR offers a unique blend of modern features and battle-proven reliability.

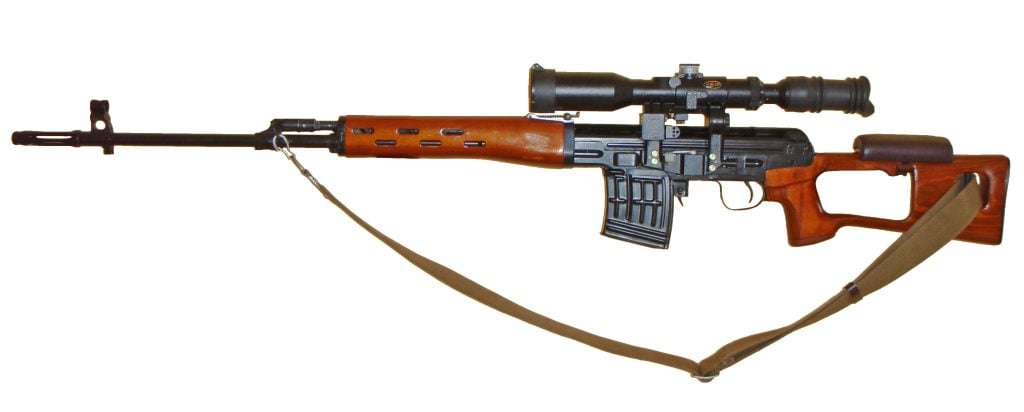
SVD Dragunov
The SVD Dragunov is an iconic sniper rifle that has been in service since 1963. Designed by Yevgeny Dragunov, this rifle became the preeminent sniper rifle of the Soviet Union and its allies. The SVD is chambered in the 7.62×54 Rimmed cartridge, known for its lethal performance and longevity. While it may not match the accuracy of modern sniper rifles, the SVD excels in its designated role as a designated marksman rifle. Its reliability, simplicity, and effectiveness have made it a favorite among snipers in various parts of the world.

HK 417/G28/M110A1
The Heckler & Koch 417 serves as the foundation for the G28 and M110A1 sniper systems used by military and law enforcement units worldwide. The HK 417 is a gas-operated short-stroke piston rifle chambered in 7.62×51 NATO (.308 Win.). It offers selective-fire capability and exceptional reliability. The G28, used by the German Bundeswehr, and the M110A1, used by the U.S. Army, are semi-automatic versions of the HK 417 optimized for precision engagements. These rifles feature advanced optics, adjustable stocks, and ambidextrous controls, making them versatile and effective sniper platforms.

Choosing the Right Sniper Rifle
Selecting the best sniper rifle depends on various factors, including mission requirements, operational environment, and personal preferences. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed decision when choosing a sniper rifle:

Mission Requirements
Different missions demand different capabilities from a sniper rifle. Consider the range, accuracy, and power needed for your specific mission. Additionally, think about the terrain and environmental conditions you will encounter. Some rifles excel in long-range engagements, while others are designed for urban operations. Assess your mission requirements thoroughly to choose the rifle that best suits your needs.
Ergonomics and Comfort
Snipers often have to remain in position for extended periods, requiring a rifle that is comfortable to use and carry. Consider the ergonomics, weight, and balance of the rifle. An adjustable stock, customizable grip, and easy-to-reach controls can enhance comfort and maneuverability in the field.
Optics and Accessories
The choice of optics and accessories can significantly impact a sniper rifle’s effectiveness. Determine the type of optics you need, such as magnification range, reticle style, and compatibility with night vision devices. Consider the availability and quality of accessories, such as bipods, suppressors, and rail systems, to ensure compatibility with your preferred rifle.
Reliability and Durability
A sniper rifle must be reliable and durable, capable of withstanding harsh conditions. Look for rifles with a proven track record and positive user feedback. Consider the rifle’s construction, materials, and overall build quality to ensure it can withstand the rigors of your operational environment.
Training and Support
Proper training and support are crucial for maximizing the potential of a sniper rifle. Consider the availability of training programs, user manuals, and support from the manufacturer or distributor. A rifle with comprehensive training resources and reliable customer support can greatly enhance your proficiency and confidence in using the weapon.
10 Best Tanks in the World 2024
Conclusion
Choosing the best sniper rifle is a critical decision for military, law enforcement, and shooting enthusiasts alike. The rifles highlighted in this guide represent some of the finest options available today, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Whether you prioritize accuracy, versatility, or ruggedness, there is a sniper rifle on this list that will meet your needs. Remember to carefully consider your mission requirements, ergonomics, optics, reliability, and training support when making your decision. With the right sniper rifle in hand, you can confidently take on the challenges of long-range engagements and achieve your objectives with precision and effectiveness.