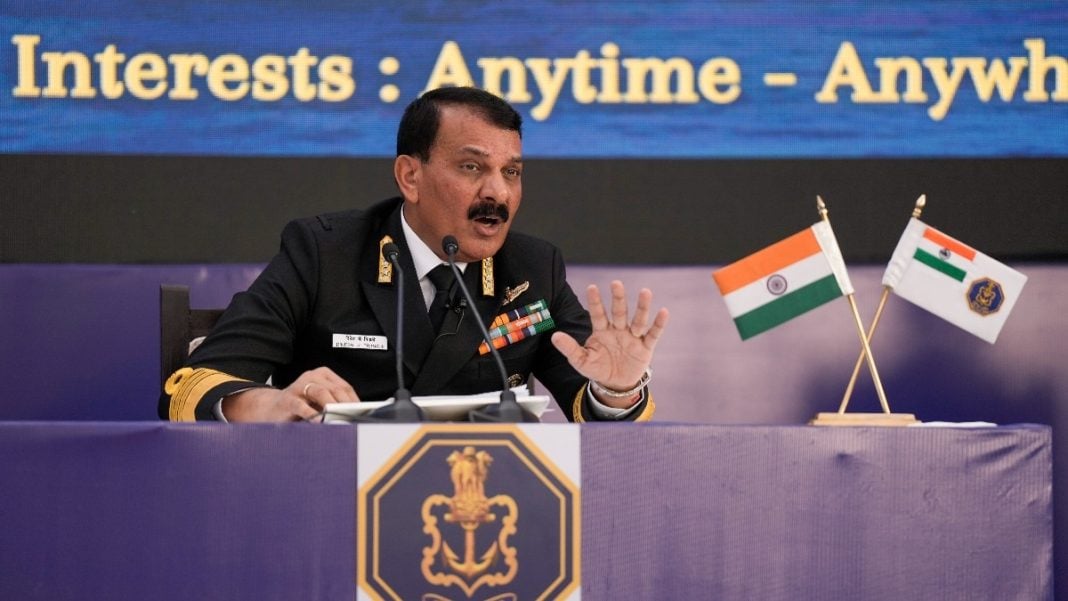
The Indian Navy is set to enhance its capabilities significantly with the government’s approval of its nuclear-powered attack submarine (SSN) program. Navy Chief Admiral Dinesh Tripathi announced on Monday that the first indigenous SSN is expected to be ready by 2036, while a second submarine from the program will be delivered within a two-year timeframe.
During the annual press conference, Admiral Tripathi emphasized that these submarines will play a crucial role in strengthening the Navy’s power projection and in safeguarding the nation’s interests. He also pointed out that this ambitious program is designed to energize the domestic defense ecosystem, thus creating opportunities for Indian industries and promoting self-reliance in defense production.
In addition to the SSN program, Admiral Tripathi remarked on the recent commissioning of INS Arighat, which serves as India’s second nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN). This new submarine marks a significant advancement in India’s nuclear deterrence capabilities. Currently undergoing trials, including missile tests, INS Arighat is being prepared for its operational role in deterrence patrols.
The Navy Chief also highlighted the achievements of INS Arihant, India’s first SSBN, which has successfully completed multiple deterrence patrols, thereby establishing a credible second-strike capability—an essential element of the nation’s nuclear strategy.
On another front, Admiral Tripathi indicated that negotiations for three additional Scorpene-class submarines, developed in partnership with France’s Naval Group under Project-75, are nearing completion, with contracts anticipated to be finalized in the next two months. With five Scorpene submarines already operational, these latest additions are expected to enhance India’s conventional underwater warfare capabilities significantly. The Scorpene submarines are characterized by their advanced stealth features and precision-strike capabilities.
Furthermore, the discussions for acquiring six more submarines under Project 75 India are also reaching advanced stages. Admiral Tripathi confirmed the successful testing of the K4 submarine-launched ballistic missile, asserting that such advancements strengthen India’s deterrent capacity.
Addressing strategic concerns, Admiral Tripathi noted the importance of India’s submarine fleet as a counterbalance to increasing maritime activities from China and Pakistan in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). While acknowledging Pakistan’s ambitious plans to expand its naval fleet to 50 ships—despite economic limitations—he expressed concern over China’s strategic investments in submarine technology aimed at global maritime dominance.
“China’s intent, resources, and vision to become a world power are clear. However, we are committed to ensuring that India’s interests remain uncompromised,” Admiral Tripathi stated. He reiterated the Navy’s focus on developing a modern, self-reliant force capable of securing Indian interests across all domains, with the submarine fleet remaining a vital component of this strategic transformation.