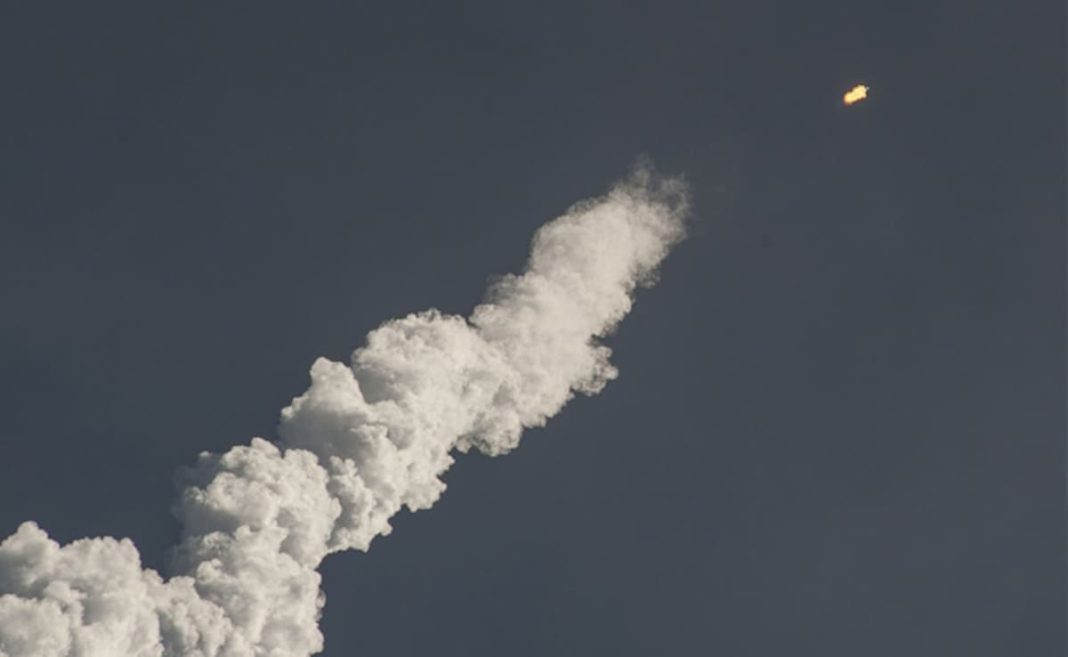
The Indian Navy achieved a significant milestone with the successful test firing of the K-4 ballistic missile from the recently commissioned nuclear submarine INS Arighaat. This event took place on Wednesday and marks a crucial advancement in the country’s defense capabilities, particularly in terms of its second-strike capability, which is essential for maintaining strategic deterrence.
The K-4 missile, which has a range of 3,500 kilometers, is designed to bolster India’s underwater offensive capabilities, ensuring that the country can respond effectively in the event of a nuclear conflict. The successful test not only validates the missile’s operational readiness but also strengthens the overall deterrent posture of the Indian Navy.
The INS Arighaat, officially inducted into service in August at the Ship Building Centre in Vishakhapatnam, is one of the two nuclear submarines currently in the Indian Navy’s fleet capable of launching ballistic missiles. The other submarine, INS Arihant, has previously demonstrated similar capabilities. Together, these submarines form an integral part of India’s nuclear triad, which includes land-based and air-based delivery systems.
Following the successful test of the K-4 missile, the navy has announced plans for additional tests of the missile system to enhance its reliability and effectiveness. This ongoing effort is part of a broader strategy to ensure that India’s defense forces are equipped with advanced technology and can respond efficiently to emerging threats.
Furthermore, the Indian Navy is expecting to augment its capabilities with the induction of a third nuclear submarine, which has already been launched and is anticipated to be commissioned next year. This expansion of the submarine fleet is seen as a pivotal step in bolstering India’s maritime security and strategic deterrence. As regional tensions continue to evolve, the Indian Navy’s advancements in underwater warfare are expected to play a crucial role in safeguarding national interests.