Infantry vs Artillery Regiments: In the world of the Indian Army, these two types of regiments play crucial roles in ground combat operations. The Artillery focuses on providing essential firepower support to the ground troops, and it can be further categorized into Field Artillery and Air Defense Artillery. On the other hand, the Infantry holds the title of being the backbone of the Indian Army, as they are the ones responsible for engaging in ground combat operations. So, if you’re interested in understanding the contrast between these two regiments, stick around as we delve into the details.
The Artillery Regiments, made up of Field Artillery and Air Defense Artillery, play an integral role by providing firepower support to the troops on the ground. Meanwhile, the Infantry Regiments form the very foundation of the Indian Army, carrying out ground combat operations. Intrigued to know more about the distinctions between Infantry and Artillery Regiments? You’ve come to the right place! Stay tuned as we explore this intriguing topic further.
Infantry Regiments
Role and Responsibilities
Infantry regiments play a crucial role in ground combat operations. As a member of an infantry regiment, your primary responsibility is to engage in direct combat with enemy forces on foot, serving as the backbone of any military operation. You are the boots on the ground, the soldiers who push through difficult terrain and hostile environments to secure objectives and protect your fellow comrades.
Your role as an infantry regiments goes beyond just engaging in direct combat. You are also responsible for reconnaissance, gathering important intelligence, and carrying out small-scale offensive and defensive operations. This can include patrolling, setting up roadblocks, and establishing a presence in key areas to maintain control and stability.
Training and Skills
To be a part of an infantry regiment, you must undergo rigorous training to develop the necessary skills and expertise. Basic military training provides you with a foundation in physical fitness, marksmanship, navigation, and communication. However, specialized infantry training takes your abilities to the next level.
You will learn advanced combat tactics, including squad and platoon-level maneuvers, urban warfare, and close-quarters combat. Additionally, you will receive training in operating a wide range of infantry-specific equipment, such as machine guns, grenade launchers, and anti-tank weapons. It is crucial to also focus on honing your physical endurance, mental resilience, and ability to make split-second decisions in high-pressure situations.
Types of Infantry Regiments
There are various types of infantry regiments that serve different purposes based on the specific needs of each military branch. Some of the most common types include light infantry, mechanized infantry, and airborne infantry.
Light infantry regiments are known for their mobility and ability to operate in highly challenging terrain, such as dense forests or mountains. They excel in conducting stealthy reconnaissance missions and surprise attacks. Mechanized infantry regiments, on the other hand, are equipped with armored vehicles to enhance their firepower and mobility. They work in close coordination with tanks and other armored units to execute offensive operations. Airborne infantry regiments specialize in parachute or helicopter insertion, allowing them to rapidly deploy behind enemy lines and establish a foothold in strategic locations.
Equipment and Weapons
As a member of an infantry regiment, you will have access to a range of weapons and equipment that are specifically designed to enhance your combat effectiveness. These include rifles (such as the INSAS, SIG 716i, TAR-21 or AK-203), machine guns (like the FN Minimi or IMI Negev NG5), and rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs). Additionally, you may be equipped with specialized gear such as body armor, night vision goggles, and portable radios for communication.
Infantry regiments also utilize various vehicles to support their operations. These can range from lightweight off-road vehicles for mobility and rapid response to armored personnel carriers that provide protection while moving through hostile areas.
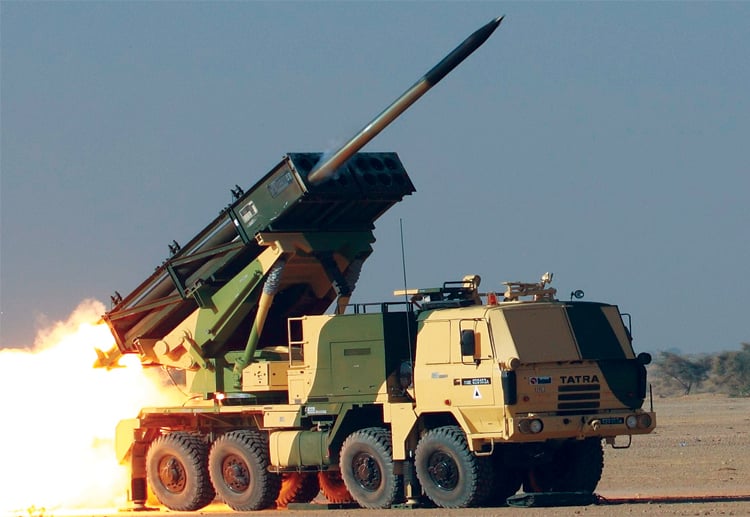

Artillery Regiments
Role and Responsibilities
Artillery regiments have a distinct role in military operations – to provide fire support to friendly forces. As a member of an artillery regiment, your primary responsibility is to operate and maintain artillery systems that deliver indirect fire against enemy targets, including troops, vehicles, and structures. Your ability to accurately and efficiently deliver firepower can significantly impact the outcome of battles and operations.
In addition to providing fire support, artillery regiments also contribute to reconnaissance and intelligence gathering by observing enemy movements and activities. This enables friendly forces to make informed decisions and adjust their tactics accordingly.
Training and Skills
Training to become a part of an artillery regiment involves mastering the technical aspects of operating artillery systems and understanding the principles of ballistics, including trajectory and range calculations. You will learn how to accurately aim and fire different types of artillery, ranging from howitzers to rocket launchers.
Moreover, you will also develop skills in coordinating with forward observers, who relay information about enemy targets and coordinate fire missions. Effective communication and teamwork are vital in artillery operations, as you must work closely with your fellow crew members to ensure accurate and timely fire support.
Types of Artillery Regiments
Similar to infantry regiments, there are several types of artillery regiments that serve specific purposes based on the needs of the military branch. Some common types include field artillery, self-propelled artillery, and rocket artillery.
Field artillery regiments utilize towed or truck-mounted howitzers to provide flexible and mobile fire support. These units can be quickly repositioned to adapt to changing battlefield conditions. Self-propelled artillery regiments, on the other hand, are equipped with armored vehicles that have integrated artillery systems. This allows for greater mobility and the ability to provide direct fire support while on the move. Rocket artillery regiments employ multiple rocket launcher systems that are capable of rapidly saturating an area with firepower, causing significant damage to enemy forces.
Equipment and Weapons
As an artillery regiment soldier, you will have access to a variety of equipment and weapons designed specifically for delivering indirect fire. This includes different calibers of artillery guns, ranging from lightweight mortars to heavy howitzers like M777, K9 Vajra. Additionally, rocket systems, such as Multiple Launch Rocket Systems (MLRS), can be utilized to deliver a devastating barrage of rockets at enemy targets.
To accurately aim and fire these systems, you will have tools such as aiming devices, ballistic computers, and communication equipment to coordinate with forward observers. Artillery regiments also utilize ammunition resupply vehicles, maintenance vehicles, and other support vehicles to sustain operations in the field.
Key Differences
Nature of Operations
While both infantry and artillery regiments play critical roles in ground combat, their nature of operations differs significantly. Infantry regiments are primarily focused on engaging in direct combat on foot, pushing through challenging terrain, and securing objectives. They often work in close quarters and are trained in various combat tactics suitable for urban environments. Artillery regiments, on the other hand, predominantly provide fire support from a distance, engaging enemy targets indirectly. They rely on their expertise in aiming and firing artillery systems accurately to neutralize threats and support friendly forces.
Functionality and Tactics
Infantry regiments predominantly rely on maneuverability and personal combat skills to achieve their objectives. They excel in small-scale offensive and defensive operations, relying on their ability to adapt quickly to changing battlefield conditions. Artillery regiments, on the other hand, focus on providing accurate and effective fire support. They employ tactics that involve coordinating with forward observers to precisely engage enemy targets, using ballistics and trajectory calculations to deliver indirect fire.
Deployment and Support
Infantry regiments are often deployed as part of larger ground forces, working alongside other combat arms such as armor and combat engineers. They frequently operate in diverse environments, ranging from dense jungles to urban centers. Artillery regiments are usually deployed in support of ground forces, establishing positions to provide fire support. They require dedicated personnel to transport and maintain their heavy equipment, often relying on logistical support to sustain operations.
Specialization and Training
Infantry regiments receive specialized training in small unit tactics, close-quarters combat, and individual soldier skills. Their training focuses on enhancing their ability to engage in direct combat effectively. In contrast, artillery regiments undergo training specific to artillery systems, including technical aspects such as aiming, firing, and calculating ballistics. They also acquire skills in coordination and communication to effectively support ground forces.
Hierarchy and Chain of Command
The hierarchy and chain of command in infantry and artillery regiments differ due to the nature of their operations. Infantry regiments often operate in small, decentralized units that require quick decision-making on the ground. This results in a flatter hierarchy, with greater reliance on individual initiative and teamwork. Artillery regiments, with an emphasis on coordination and precise fire support, typically have a more structured chain of command to ensure efficient communication and proper execution of fire missions.
Similarities
Role in Ground Combat
While infantry and artillery regiments have distinct roles, both are essential components of ground combat operations. Infantry regiments engage in direct combat, securing objectives and engaging enemy forces directly, while artillery regiments provide fire support to assist and protect friendly forces. Together, they contribute to the overall effectiveness and success of ground operations.
Importance in Military Operations
Both infantry and artillery regiments hold significant importance in military operations. Infantry regiments provide the essential boots on the ground, offering a physical presence and the capability to engage directly with enemy forces. Artillery regiments, with their ability to deliver accurate and lethal firepower, serve as a force multiplier, providing crucial support to ground forces and helping to neutralize or suppress enemy threats.
Integration and Cooperation
Infantry and artillery regiments often work hand in hand, relying on each other’s capabilities and expertise. Infantry regiments depend on the fire support provided by artillery regiments to suppress enemy positions and create favorable conditions for their own operations. Artillery regiments, in turn, rely on the intelligence and situational awareness provided by the infantry regiments to accurately engage enemy targets. Integration and cooperation between these two forces are crucial for successful ground combat operations.
Conclusion
Infantry and artillery regiments may have different roles and responsibilities, but they are both vital in ground combat operations. As a member of an infantry regiment, you will engage in direct combat, securing objectives and providing a physical presence on the ground. Artillery regiments, on the other hand, provide crucial fire support, neutralizing enemy targets and protecting friendly forces. Both regiments rely on their specialized training, skills, and equipment to carry out their missions effectively. Together, they represent the core components of ground combat operations, working hand in hand to achieve success in military operations.